ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Feb 2018
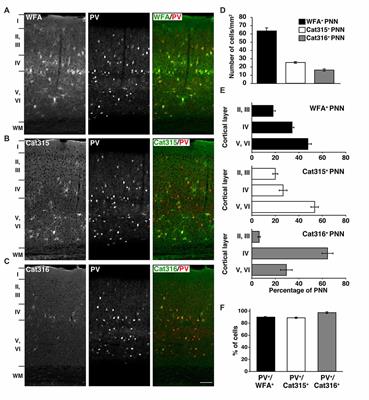
Structural Variation of Chondroitin Sulfate Chains Contributes to the Molecular Heterogeneity of Perineuronal Nets
doi 10.3389/fnint.2018.00003
- 5,932 views
- 58 citations
10k
Total downloads
62k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Feb 2018

REVIEW
Published on 01 Dec 2017

REVIEW
Published on 23 Oct 2017
REVIEW
Published on 17 Oct 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 30 Aug 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Aug 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Aug 2017
