EDITORIAL
Published on 18 Apr 2024
Editorial: Kidney transplant patients with COVID-19 infection
doi 10.3389/frtra.2024.1407254
- 368 views
2,984
Total downloads
10k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 18 Apr 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
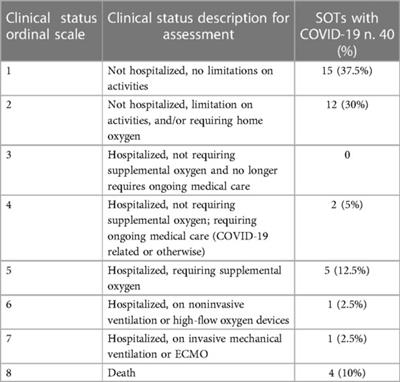
Published on 12 Mar 2024
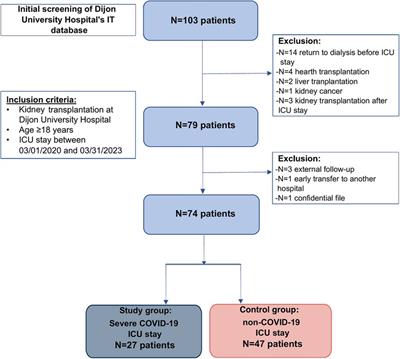
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 Nov 2023
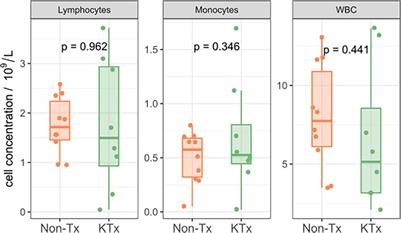
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 19 Sep 2023
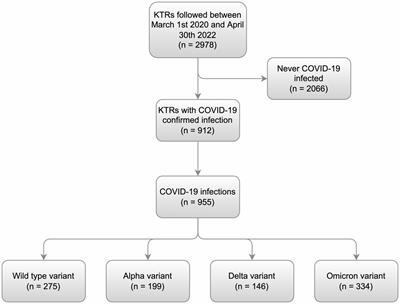
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 Mar 2023
CASE REPORT
Published on 23 Mar 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 16 Mar 2023