EDITORIAL
Published on 23 Jan 2018
Editorial: Single-Domain Antibodies—Biology, Engineering and Emerging Applications
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00041
- 3,284 views
- 8 citations
66k
Total downloads
329k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 23 Jan 2018
TECHNOLOGY REPORT
Published on 23 Jan 2018
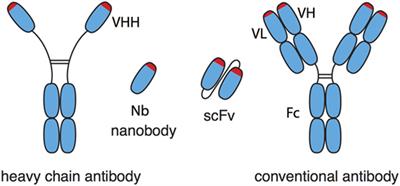
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Dec 2017

REVIEW
Published on 13 Dec 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 Dec 2017

REVIEW
Published on 08 Dec 2017

PERSPECTIVE
Published on 20 Nov 2017

REVIEW
Published on 02 Nov 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 30 Oct 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Oct 2017
PERSPECTIVE
Published on 12 Oct 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Oct 2017
