EDITORIAL
Accepted on 11 Mar 2025
Editorial: Pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients with congenital heart disease: areas of controversy and the role of genetics
doi 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1589305
1,798
Total downloads
8,014
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Accepted on 11 Mar 2025
CASE REPORT
Published on 29 Nov 2024
REVIEW
Published on 09 May 2024
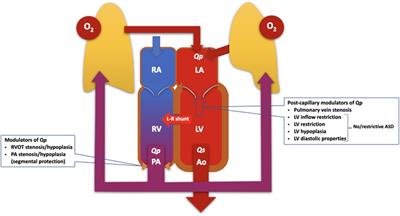
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Feb 2024
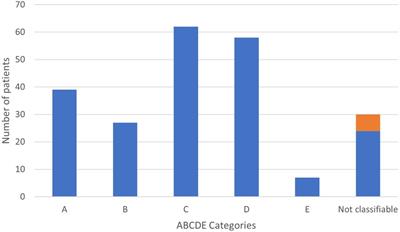
CASE REPORT
Published on 23 Oct 2023