EDITORIAL
Published on 18 Dec 2024
Editorial: Drivers of antimicrobial resistance during and after COVID-19 pandemic in low-middle-income countries
doi 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1521798
- 244 views
5,939
Total downloads
24k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 18 Dec 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 27 Sep 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 Sep 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Jul 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Jul 2024

STUDY PROTOCOL
Published on 01 Feb 2024
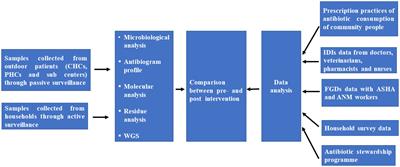
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Jan 2024

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 18 Dec 2023

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 Jun 2023