MINI REVIEW
Published on 31 Aug 2023
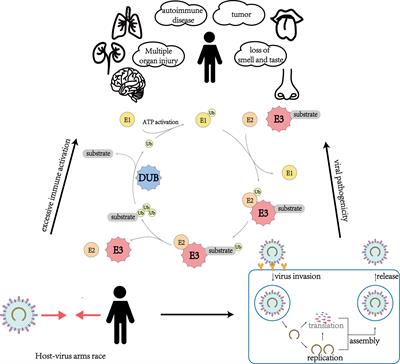
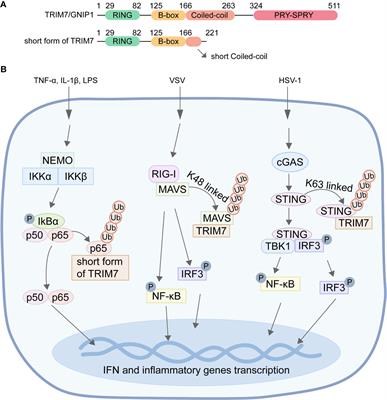
Interplay between TRIM7 and antiviral immunity
doi 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1256882
- 2,144 views
- 6 citations
2,288
Total downloads
7,789
Total views and downloads
MINI REVIEW
Published on 31 Aug 2023

MINI REVIEW
Published on 09 Jun 2023