EDITORIAL
Published on 26 Sep 2023
Editorial: Antimicrobial resistance in pediatric infectious diseases: antimicrobial resistance, resistance mechanisms and antimicrobial use
doi 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1287051
- 3,355 views
- 3 citations
17k
Total downloads
74k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
EDITORIAL
Published on 26 Sep 2023
REVIEW
Published on 10 Aug 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 Jul 2023
CASE REPORT
Published on 21 Jun 2023
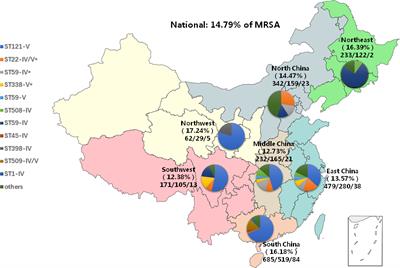
REVIEW
Published on 15 Jun 2023
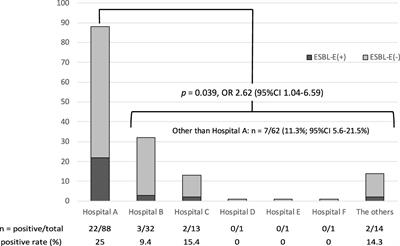
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 Jun 2023
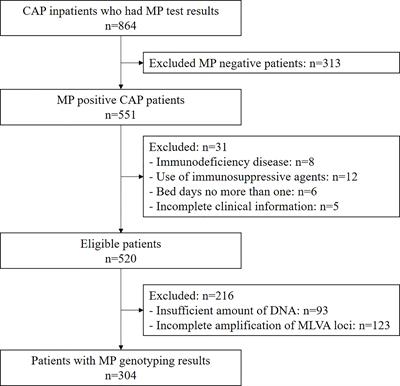
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 Jun 2023
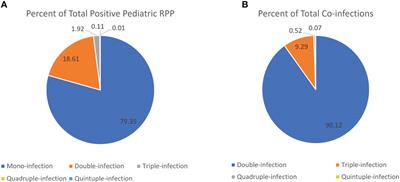
REVIEW
Published on 13 Jun 2023
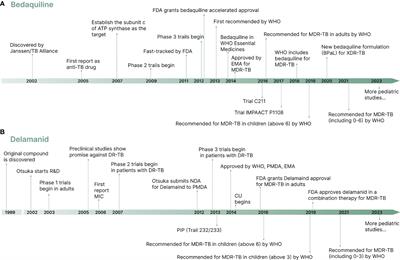
MINI REVIEW
Published on 02 Jun 2023
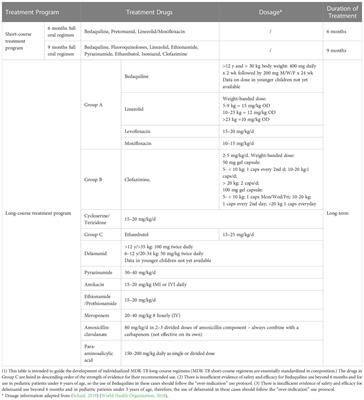
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 May 2023
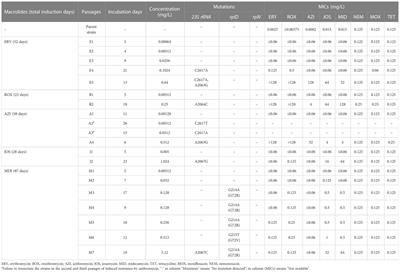
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 May 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 May 2023