ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Feb 2025
Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by a small molecule targeting CK1α–β-catenin–NF-κB and CK1α–NRF2–mitochondrial OXPHOS pathways during mycobacterial infection
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1553093
- 167 views
11k
Total downloads
44k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Feb 2025
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 27 Nov 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Nov 2024
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 16 Jul 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 07 Nov 2023

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Nov 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 24 May 2023
OPINION
Published on 23 May 2023
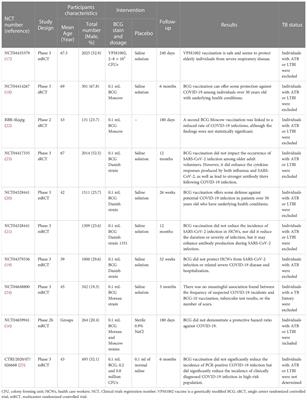
REVIEW
Published on 31 Mar 2023
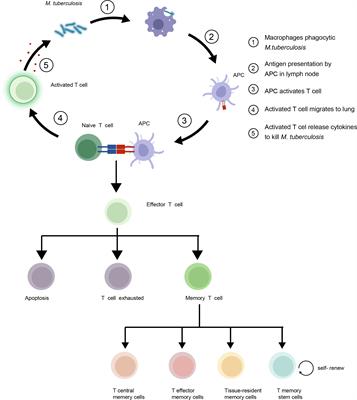
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 Feb 2023
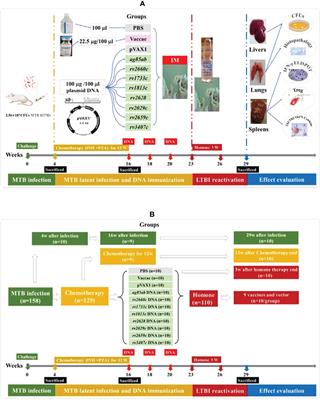
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Feb 2023
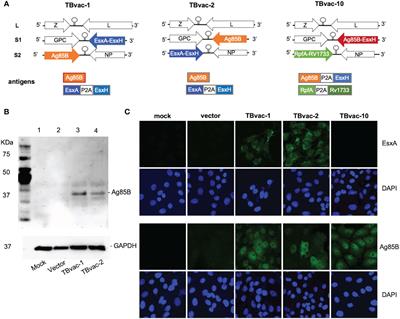
REVIEW
Published on 31 Jan 2023