ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Oct 2023
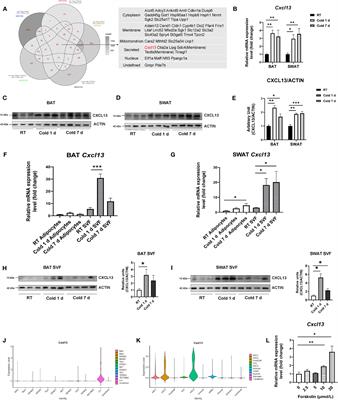
CXCL13 promotes thermogenesis in mice via recruitment of M2 macrophage and inhibition of inflammation in brown adipose tissue
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1253766
- 2,476 views
- 6 citations
20k
Total downloads
53k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Oct 2023

REVIEW
Published on 17 Oct 2023
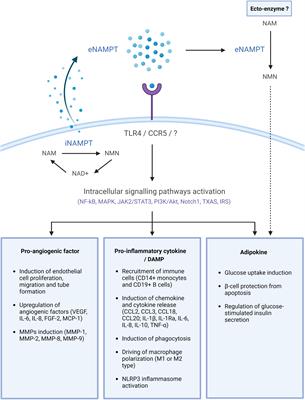
MINI REVIEW
Published on 26 Sep 2023
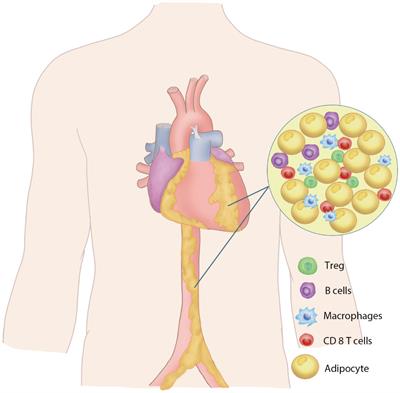
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Jul 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Dec 2022
REVIEW
Published on 24 Nov 2022

REVIEW
Published on 21 Nov 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 18 Nov 2022