EDITORIAL
Published on 19 Aug 2024
Editorial: Self-assembly of biomolecules as healthcare materials: drug delivery and beyond
doi 10.3389/fchem.2024.1473033
- 413 views
5,587
Total downloads
31k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 19 Aug 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Sep 2023
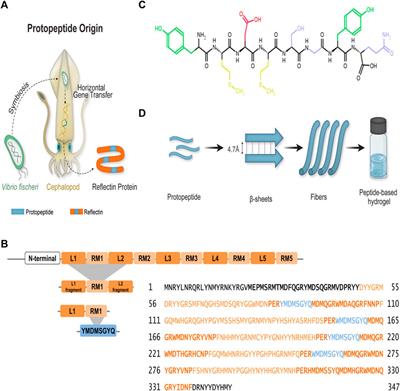
REVIEW
Published on 25 Jan 2023
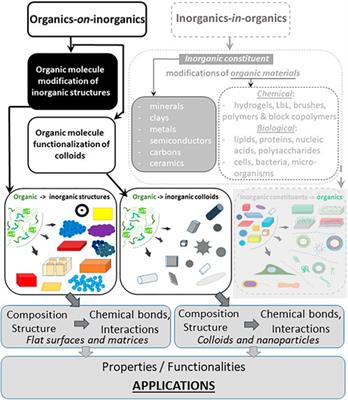
MINI REVIEW
Published on 06 Jan 2023
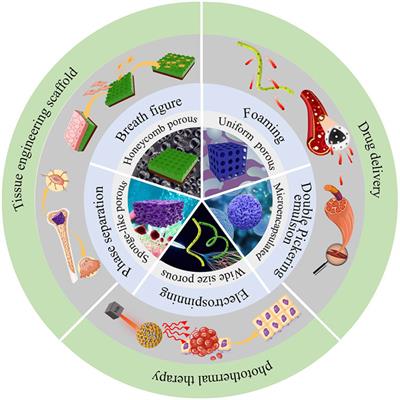
MINI REVIEW
Published on 24 Nov 2022
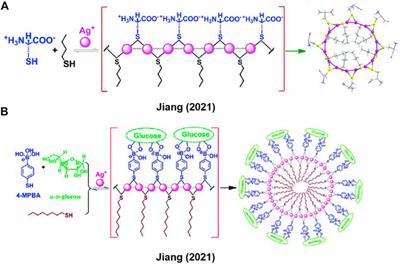
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Sep 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 24 Aug 2022
![Cucurbit [8] uril-based supramolecular fluorescent biomaterials for cytotoxicity and imaging studies of kidney cells](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/myhome article library/974607/974607_Thumb_400.jpg)