EDITORIAL
Published on 26 Jun 2023
Editorial: The immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and strategies to revert its immune regulatory milieu for cancer immunotherapy
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1238698
- 1,192 views
- 4 citations
23k
Total downloads
63k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 26 Jun 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Jun 2023

REVIEW
Published on 24 Mar 2023

REVIEW
Published on 06 Feb 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Feb 2023
REVIEW
Published on 27 Jan 2023
REVIEW
Published on 20 Jan 2023

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 19 Jan 2023
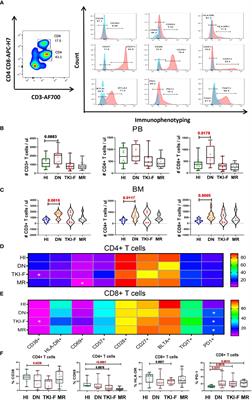
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 18 Jan 2023

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Jan 2023

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 05 Jan 2023

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 Dec 2022