REVIEW
Published on 26 Jul 2017
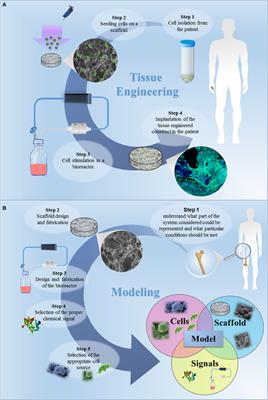
Tissue Engineering Approaches in the Design of Healthy and Pathological In Vitro Tissue Models
doi 10.3389/fbioe.2017.00040
- 56,054 views
- 235 citations
15k
Total downloads
104k
Total views and downloads
REVIEW
Published on 26 Jul 2017

REVIEW
Published on 15 Nov 2016

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 30 Sep 2016

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Dec 2014