ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 19 Jul 2023
Effect of silkworm pupae (Bombyx mori) protein on colon cancer in nude mice: inhibition of tumor growth, oxidative stress and inflammatory response

doi 10.3389/fphar.2023.1138742
- 1,842 views
- 9 citations
6,880
Total downloads
28k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 19 Jul 2023

REVIEW
Published on 03 May 2023
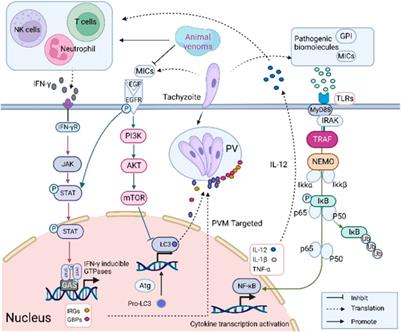
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Mar 2023

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 Mar 2023
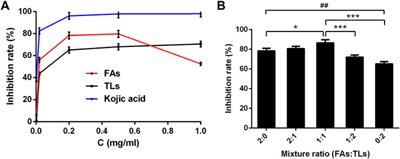
REVIEW
Published on 06 Oct 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 Sep 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 19 Jan 2022

