EDITORIAL
Published on 19 Jul 2024
Editorial: Deregulated signaling pathways in inflammation and cancer
doi 10.3389/fcell.2024.1459926
- 541 views
7,990
Total downloads
27k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 19 Jul 2024
REVIEW
Published on 17 Apr 2024
REVIEW
Published on 06 Dec 2023
MINI REVIEW
Published on 04 Aug 2023
REVIEW
Published on 08 Feb 2023
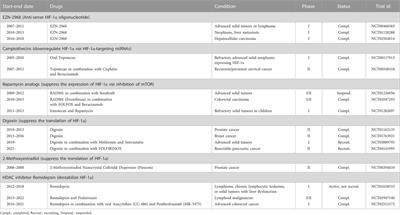
REVIEW
Published on 12 Dec 2022
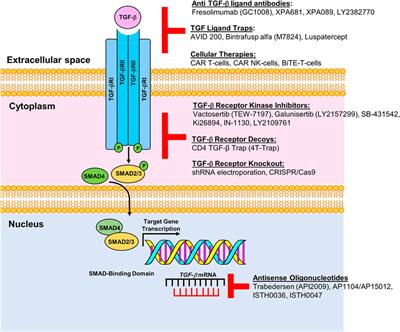
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 Oct 2022
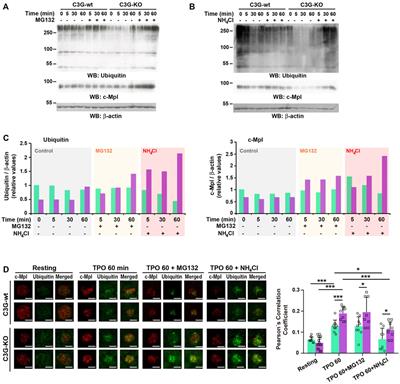
REVIEW
Published on 19 Aug 2022