ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Mar 2023
Digitizing tuberculosis treatment monitoring in Wuhan city, China, 2020–2021: Impact on medication adherence

doi 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1033532
- 1,745 views
- 3 citations
14k
Total downloads
42k
Total views and downloads
Select the journal/section where you want your idea to be submitted:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Mar 2023

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 27 Jan 2023
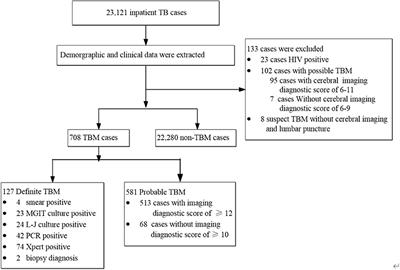
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 26 Jan 2023

CLINICAL TRIAL
Published on 26 Jan 2023
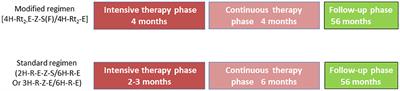
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 Dec 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 29 Nov 2022
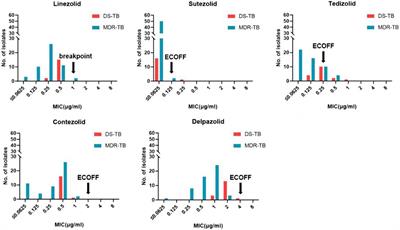
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 24 Nov 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Nov 2022
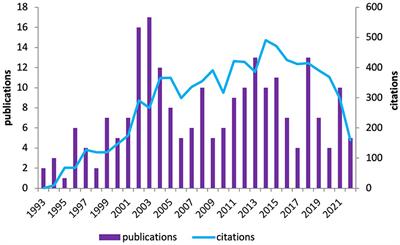
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Nov 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Nov 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Nov 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Oct 2022


Frontiers in Medicine
Infectious Diseases – Surveillance, Prevention and TreatmentOffline