SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Published on 23 Nov 2023
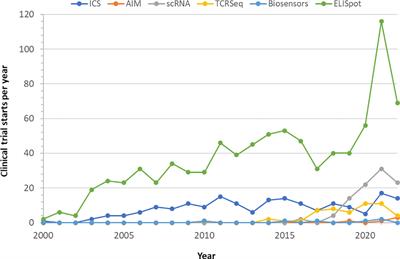
Integrated antibody and cellular immunity monitoring are required for assessment of the long term protection that will be essential for effective next generation vaccine development
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1166059
- 1,609 views
- 4 citations