EDITORIAL
Published on 13 Dec 2017
Editorial: Natural Antibodies in Health and Disease
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01795
- 8,803 views
- 12 citations
22k
Total Downloads
130k
Total Views and Downloads
Select the journal/section where you want your idea to be submitted:
EDITORIAL
Published on 13 Dec 2017
PERSPECTIVE
Published on 26 Jul 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 Jun 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 Mar 2017

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Nov 2016

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 Nov 2016
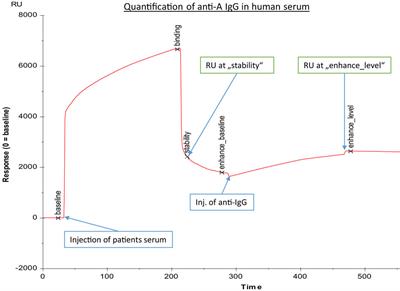
METHODS
Published on 04 Nov 2016

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Sep 2016

REVIEW
Published on 09 Sep 2016
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 Aug 2016

REVIEW
Published on 06 Jun 2016

MINI REVIEW
Published on 11 Apr 2016

Frontiers in Public Health
Vaccines and Molecular TherapeuticsOffline