EDITORIAL
Published on 16 May 2023
Editorial: Causative mechanism and potential pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
doi 10.3389/fneur.2023.1199840
- 1,145 views
10k
Total downloads
28k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
EDITORIAL
Published on 16 May 2023
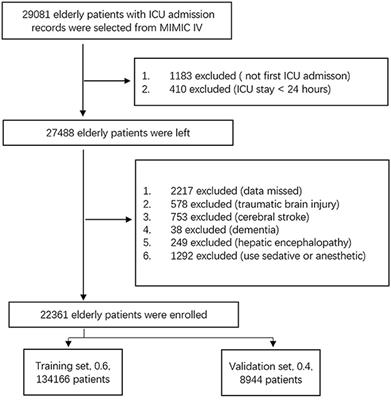
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Feb 2023
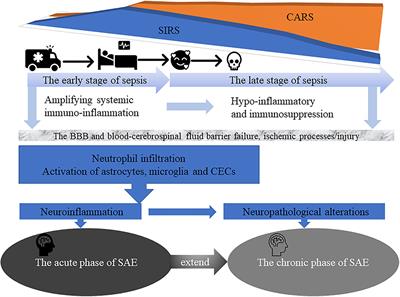
REVIEW
Published on 29 Sep 2022
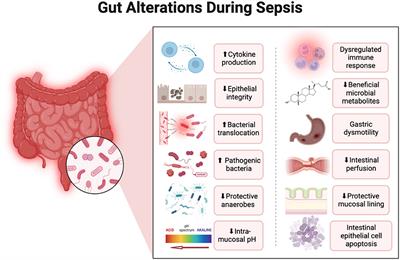
REVIEW
Published on 27 Jun 2022
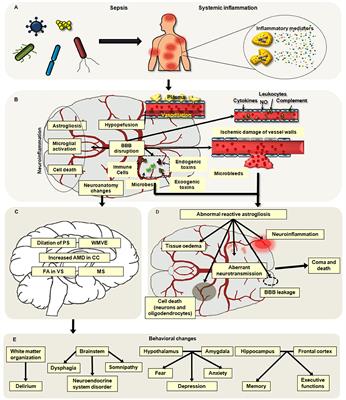
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 Jun 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 16 May 2022
REVIEW
Published on 16 Mar 2022