EDITORIAL
Published on 03 Nov 2022
Editorial: Oxidative stress related to cellular metabolism in lung health and diseases
doi 10.3389/fphar.2022.1015423
- 1,468 views
- 4 citations
9,765
Total downloads
34k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 03 Nov 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Jul 2022
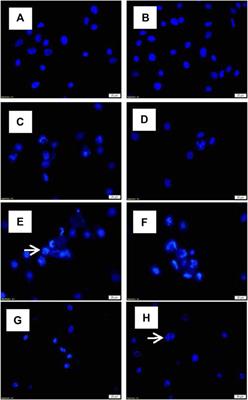
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 Jul 2022
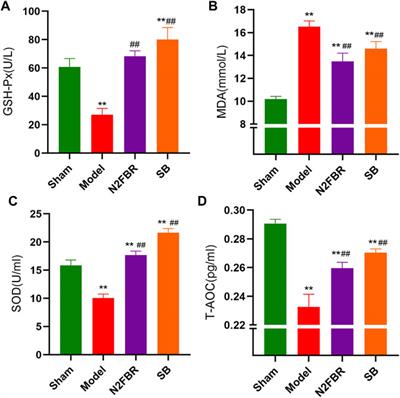
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Jun 2022
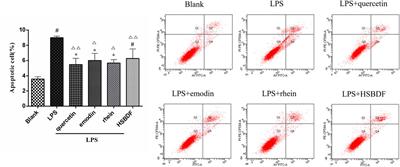
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Jun 2022
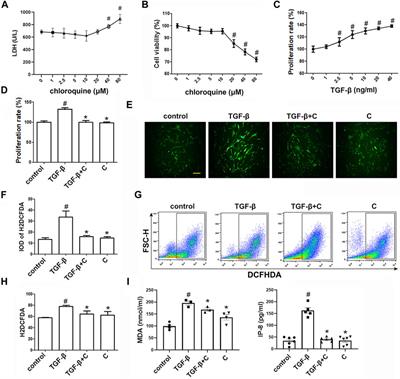
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 May 2022
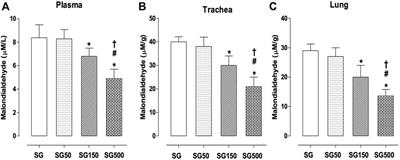
REVIEW
Published on 26 Apr 2022
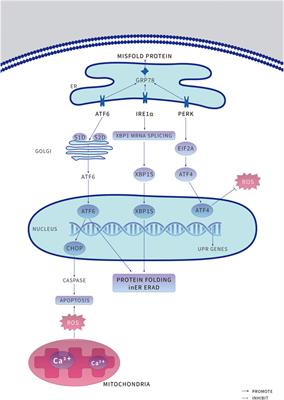
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 Apr 2022
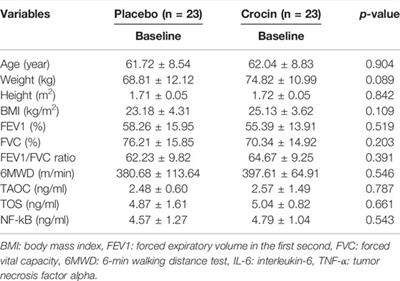
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 19 Apr 2022
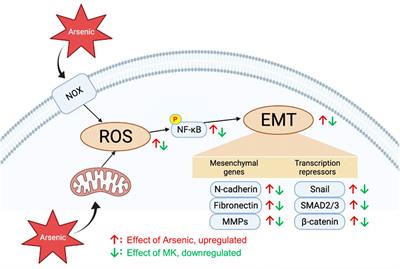
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 24 Jan 2022
