EDITORIAL
Published on 13 Jan 2023
Editorial: Impact of tumor microenvironment on lung cancer
doi 10.3389/fonc.2023.1136803
- 704 views
8,450
Total downloads
25k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
EDITORIAL
Published on 13 Jan 2023
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Published on 02 Jun 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Apr 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Feb 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Jul 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 May 2021
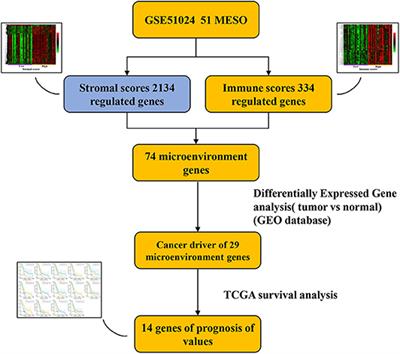
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 03 Mar 2021
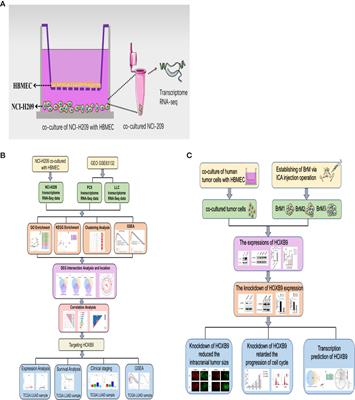
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 27 Oct 2020

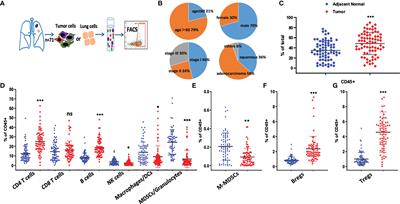
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 16 Sep 2020