ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Oct 2022
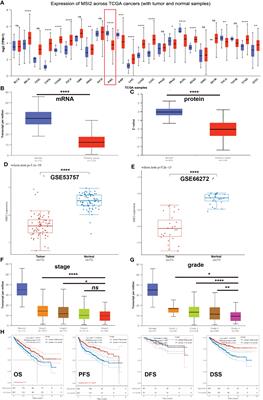
Increased expression of the RNA-binding protein Musashi-2 is associated with immune infiltration and predicts better outcomes in ccRCC patients
doi 10.3389/fonc.2022.949705
- 2,079 views
- 5 citations
44k
Total downloads
124k
Total views and downloads
Select the journal/section where you want your idea to be submitted:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Oct 2022

REVIEW
Published on 02 Sep 2022
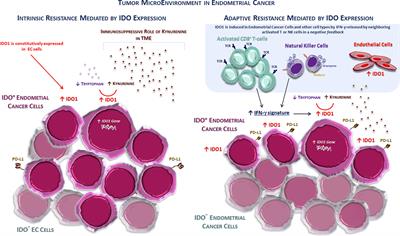
REVIEW
Published on 07 Jul 2022

REVIEW
Published on 06 Jul 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 29 Jun 2022

MINI REVIEW
Published on 28 Jun 2022
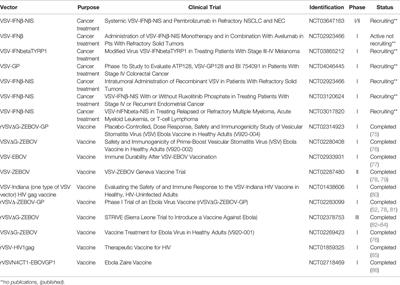
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 May 2022

CORRECTION
Published on 04 May 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Apr 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 Apr 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 Mar 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Feb 2022


Frontiers in Oncology