ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Jun 2023
Assessment of interleukin-10 promoter variant (−1082A/G) and cytokine production in patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome

doi 10.3389/fped.2023.1210158
- 1,551 views
- 2 citations
4,711
Total downloads
17k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Jun 2023

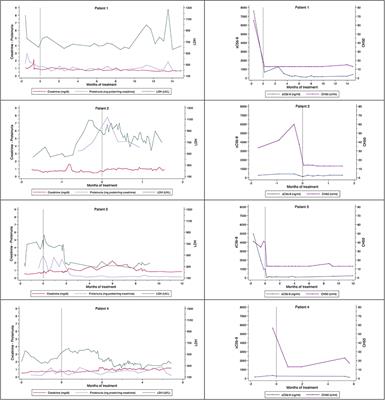
CASE REPORT
Published on 15 Feb 2023
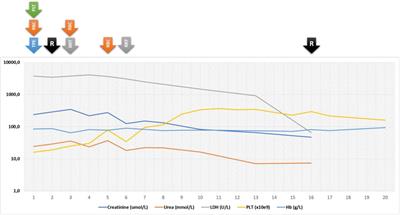
CASE REPORT
Published on 01 Aug 2022
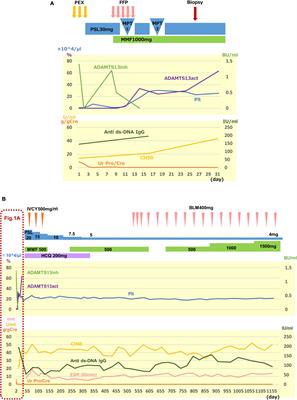
CASE REPORT
Published on 04 Jul 2022
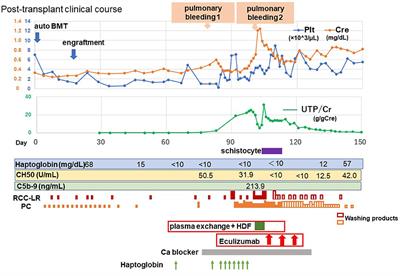
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 11 Nov 2021