REVIEW
Published on 15 Jun 2023
Pathophysiology and management of liver cirrhosis: from portal hypertension to acute-on-chronic liver failure
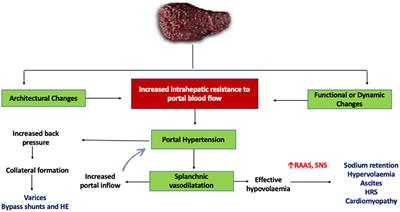
doi 10.3389/fmed.2023.1060073
- 40,412 views
- 13 citations
12k
Total downloads
71k
Total views and downloads
REVIEW
Published on 15 Jun 2023

REVIEW
Published on 09 Jan 2023
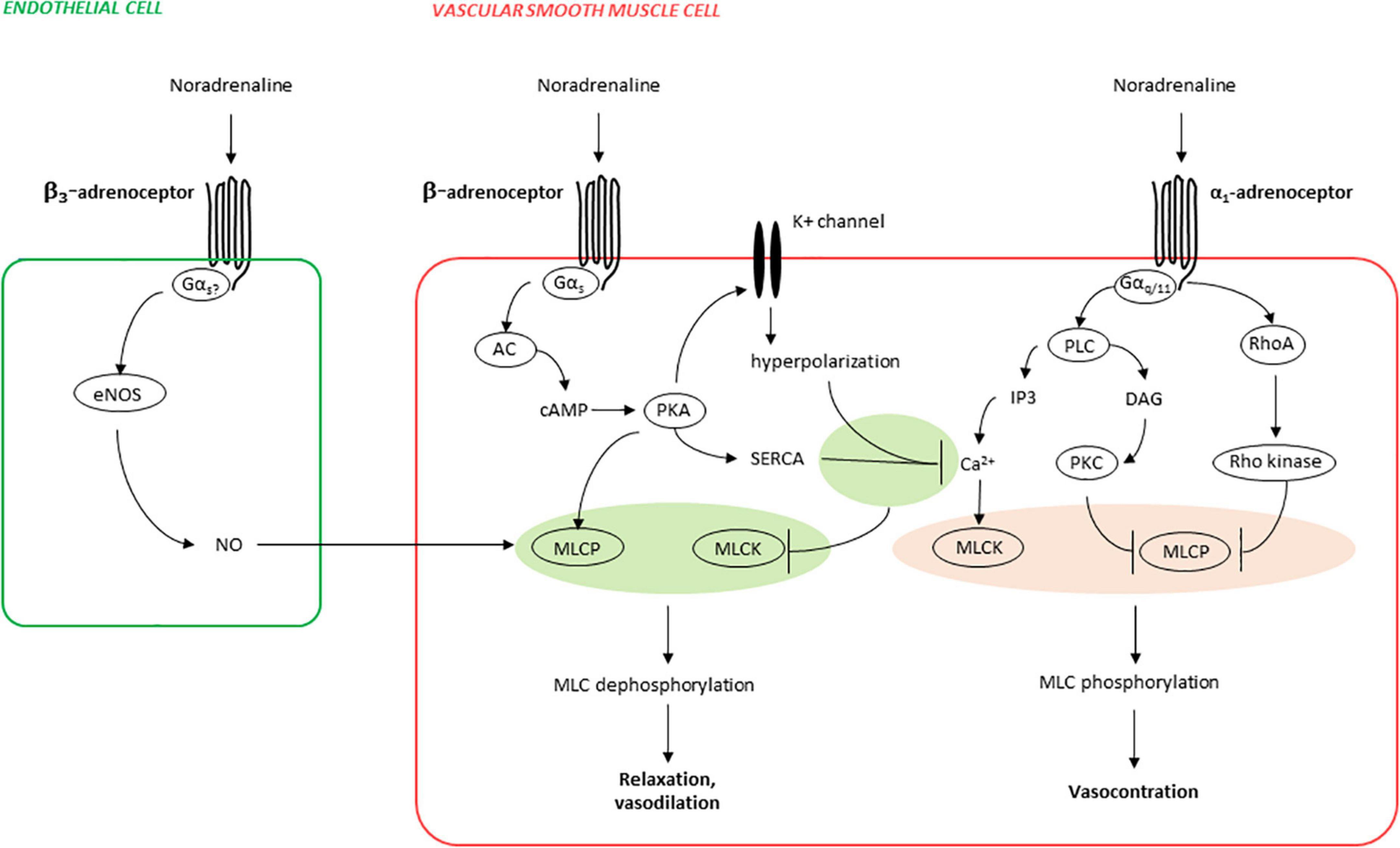
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Dec 2022
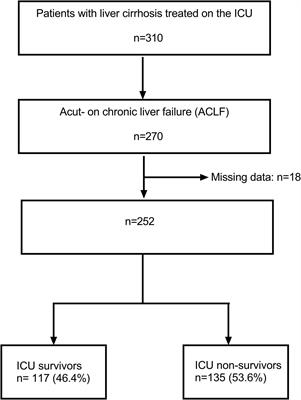
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 Oct 2022
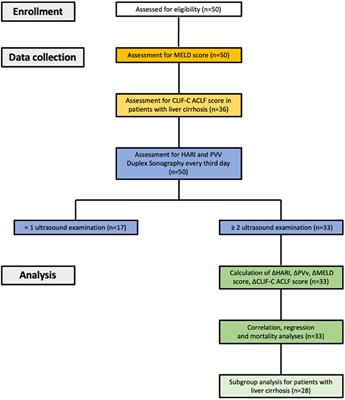
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 29 Sep 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Jun 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 Apr 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Apr 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 Mar 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 11 Feb 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Jan 2022
