ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 May 2022
Pre-processing of Sub-millimeter GE-BOLD fMRI Data for Laminar Applications
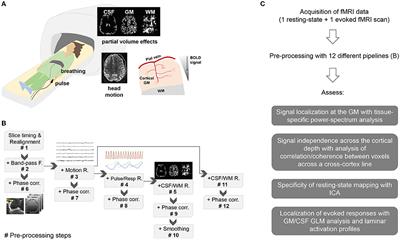
doi 10.3389/fnimg.2022.869454
- 1,870 views
- 4 citations
4,925
Total downloads
26k
Total views and downloads
Select the journal/section where you want your idea to be submitted:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 May 2022

TECHNOLOGY AND CODE
Published on 11 Mar 2022
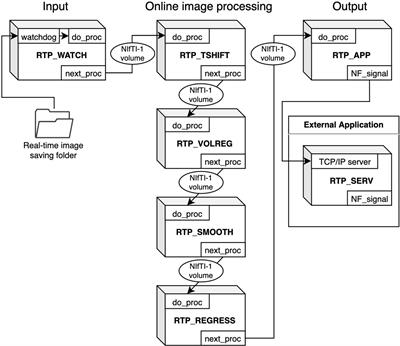
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 16 Feb 2022
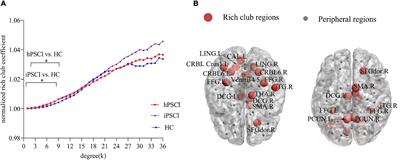
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 28 Dec 2021
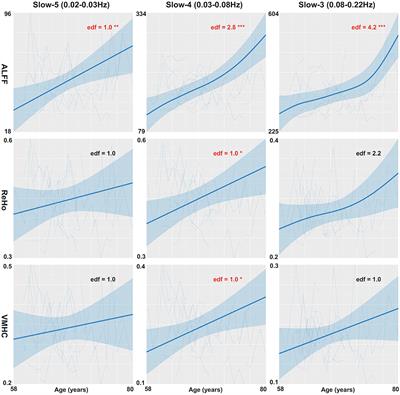
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 27 Dec 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 30 Nov 2021

Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience
Frontiers in Neuroimaging