EDITORIAL
Published on 01 Aug 2023
Editorial: The role of TNF-TNFR2 signal in immunosuppressive cells and its therapeutic implications, volume II
doi 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1227003
- 996 views
16k
Total downloads
56k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
EDITORIAL
Published on 01 Aug 2023
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Published on 16 Nov 2022
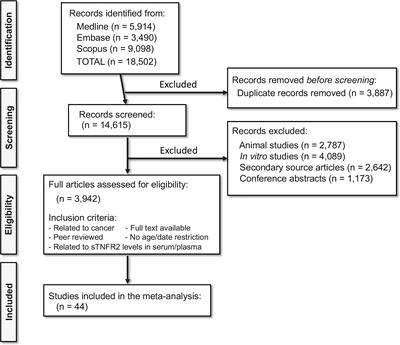
REVIEW
Published on 07 Jul 2022

PERSPECTIVE
Published on 30 Jun 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 Jun 2022

REVIEW
Published on 16 May 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Apr 2022

REVIEW
Published on 17 Feb 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 16 Feb 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Dec 2021

