EDITORIAL
Published on 26 Sep 2022
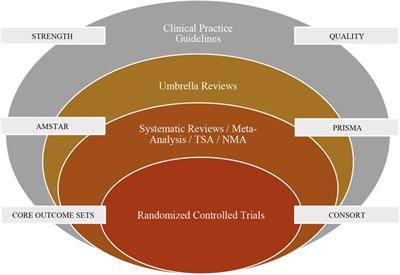
Editorial: Integration of evidence-based research and practice in preventive and pediatric dentistry
doi 10.3389/froh.2022.1017226
- 1,192 views
- 2 citations
4,341
Total downloads
16k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 26 Sep 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Sep 2022

MINI REVIEW
Published on 18 Jul 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Jul 2022

