EDITORIAL
Published on 13 Dec 2022
Editorial: Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury: Mechanisms, pathogenesis, and potential therapeutic strategies
doi 10.3389/fncel.2022.1086692
- 1,107 views
- 3 citations
4,895
Total downloads
23k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 13 Dec 2022
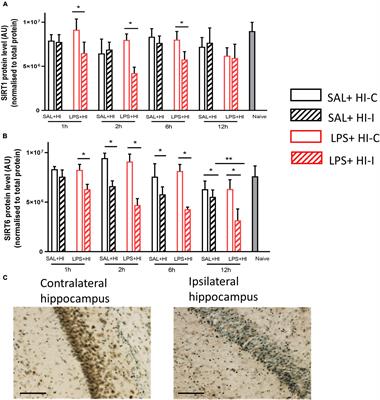
REVIEW
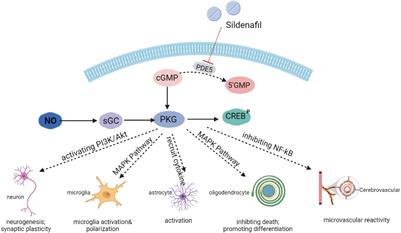
Published on 10 May 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
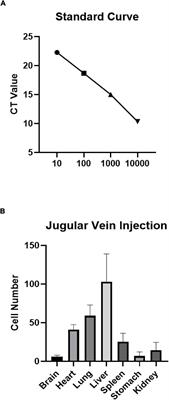
Published on 02 Mar 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
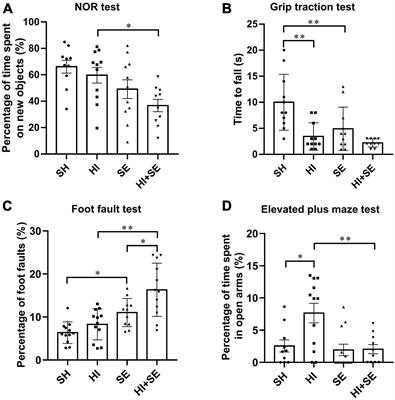
Published on 18 Feb 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Dec 2021
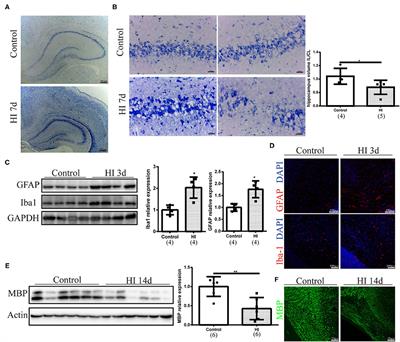
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Nov 2021