ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Sep 2022
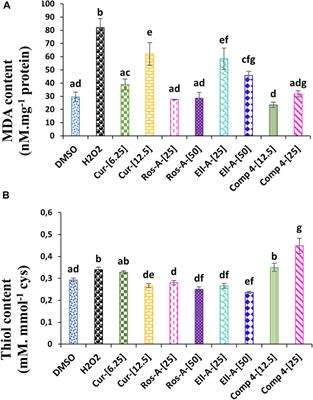
Synergistic antioxidant effects of natural compounds on H2O2-induced cytotoxicity of human monocytes
doi 10.3389/fphar.2022.830323
- 3,427 views
- 11 citations
3,345
Total downloads
16k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Sep 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 Jun 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Jan 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Jan 2022
