EDITORIAL
Published on 23 Sep 2022
Editorial: The role of autophagy in infectious diseases
doi 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1039282
- 1,032 views
- 4 citations
16k
Total downloads
57k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
EDITORIAL
Published on 23 Sep 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Aug 2022
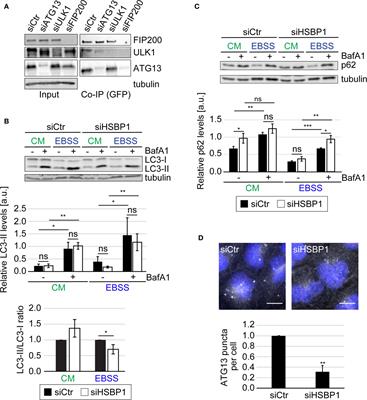
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Apr 2022
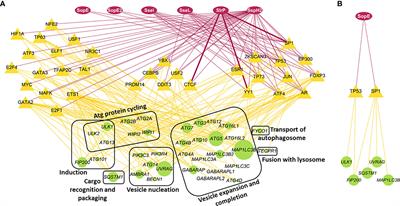
REVIEW
Published on 24 Mar 2022
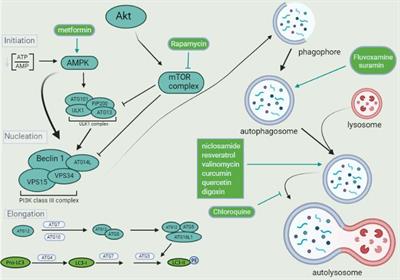
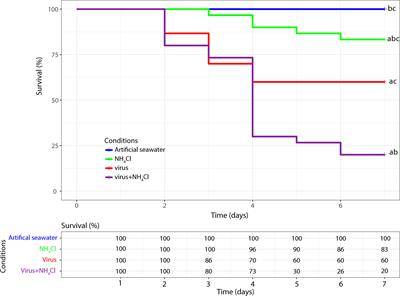
PERSPECTIVE
Published on 17 Mar 2022
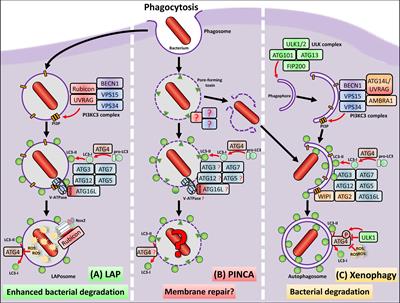
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Feb 2022
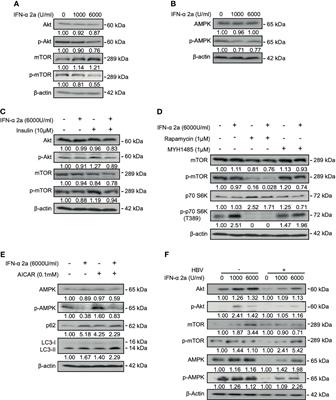
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 25 Jan 2022
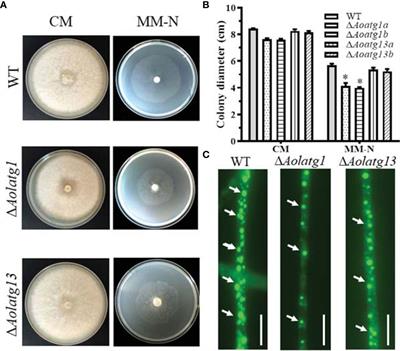
MINI REVIEW
Published on 05 Jan 2022
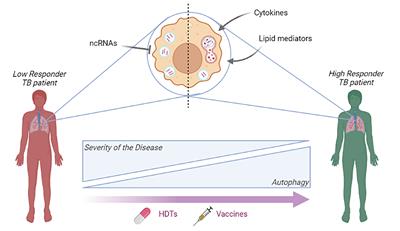
REVIEW
Published on 03 Jan 2022
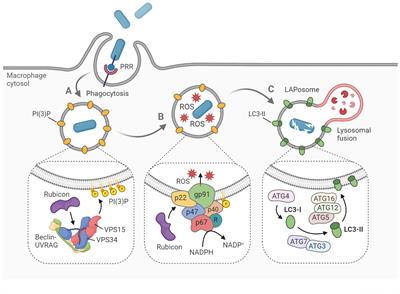
REVIEW
Published on 03 Jan 2022
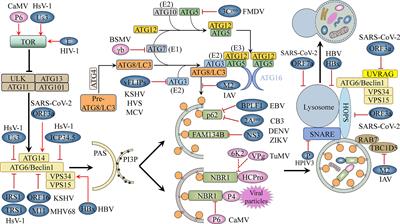
REVIEW
Published on 02 Dec 2021
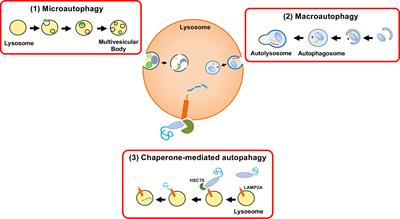
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 15 Nov 2021