REVIEW
Published on 12 May 2022
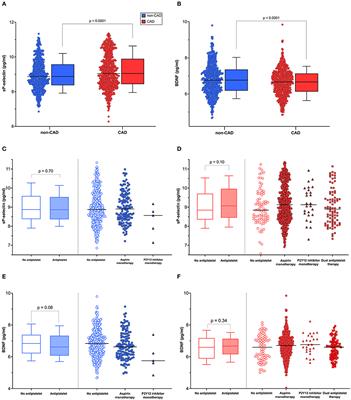
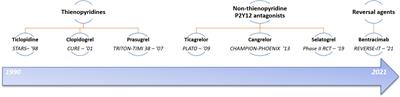
P2Y12 Antagonists in Cardiovascular Disease—Finding the Best Balance Between Preventing Ischemic Events and Causing Bleeding
doi 10.3389/fcvm.2022.854813
- 2,493 views
- 2 citations
14k
Total downloads
42k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
REVIEW
Published on 12 May 2022

CASE REPORT
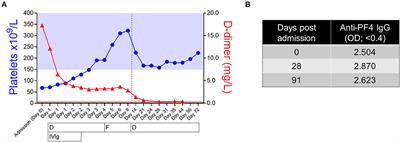
Published on 09 Feb 2022
REVIEW
Published on 28 Jan 2022
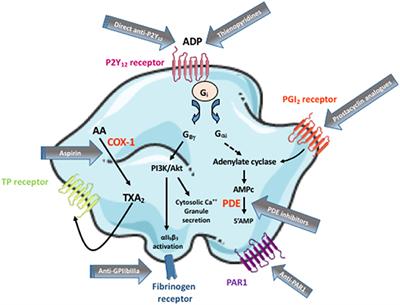
MINI REVIEW
Published on 06 Jan 2022
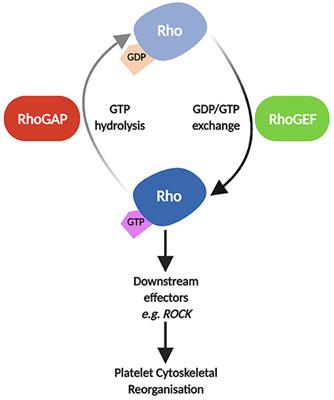
MINI REVIEW
Published on 25 Nov 2021
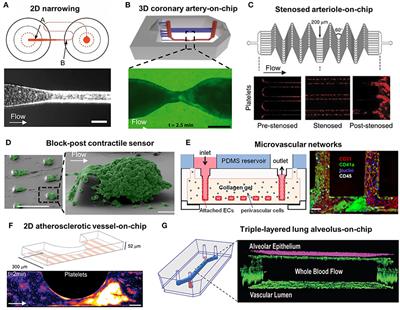
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 07 Sep 2021