EDITORIAL
Published on 12 Jan 2023
Editorial: Modulation of neuronal excitability by non-neuronal cells in physiological and pathophysiological conditions
doi 10.3389/fncel.2023.1133445
- 1,135 views
- 2 citations
8,604
Total downloads
31k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 12 Jan 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Dec 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Jul 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Jan 2022
MINI REVIEW
Published on 16 Dec 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Dec 2021
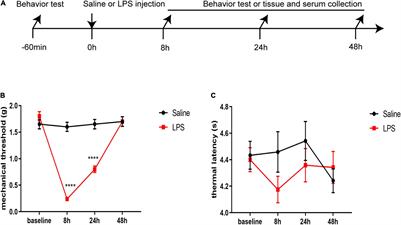
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Dec 2021
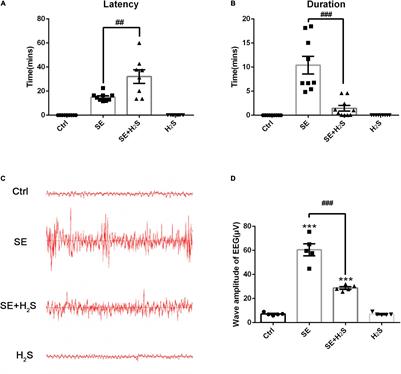
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Nov 2021
