EDITORIAL
Published on 17 Oct 2022
Editorial: Epigenomic polymorphisms: The drivers of diversity and heterogeneity
doi 10.3389/fgene.2022.1008178
- 866 views
10k
Total downloads
47k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 17 Oct 2022
REVIEW
Published on 18 May 2022
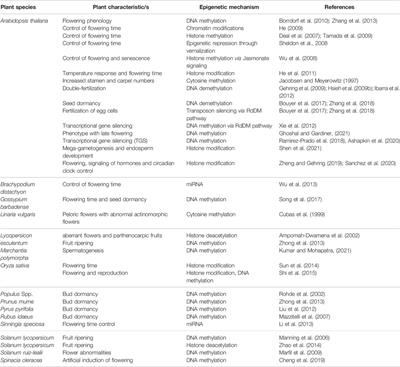
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 May 2022
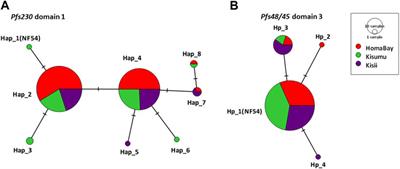
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 May 2022
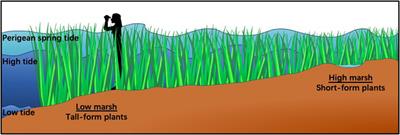
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 May 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 03 Mar 2022
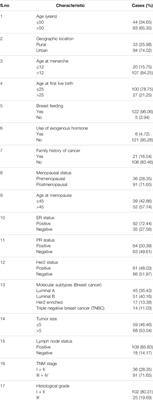
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 03 Feb 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 29 Nov 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Jun 2021

REVIEW
Published on 15 Jul 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 Apr 2019

