ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 19 Jul 2022
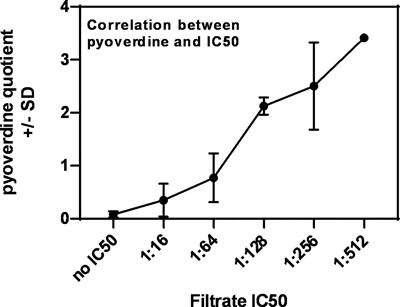
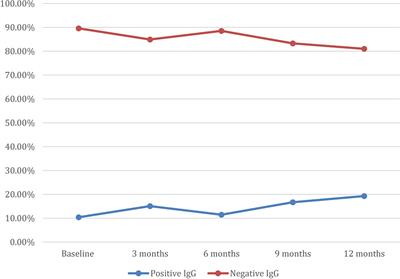
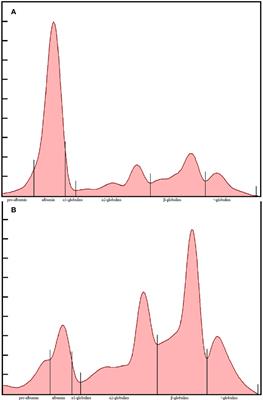
Challenges to establish the diagnosis of aspergillosis in non-laboratory animals: looking for alternatives in veterinary medicine and demonstration of feasibility through two concrete examples in penguins and dolphins
doi 10.3389/fcimb.2022.757200
- 1,821 views
- 4 citations