EDITORIAL
Published on 09 Sep 2022
Editorial: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): Is it time for MRD-driven treatment?
doi 10.3389/fonc.2022.1020185
- 1,062 views
- 1 citation
7,056
Total downloads
20k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
EDITORIAL
Published on 09 Sep 2022
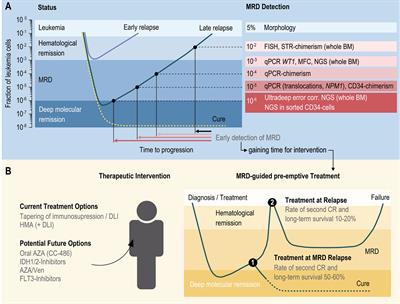
REVIEW
Published on 18 Jul 2022
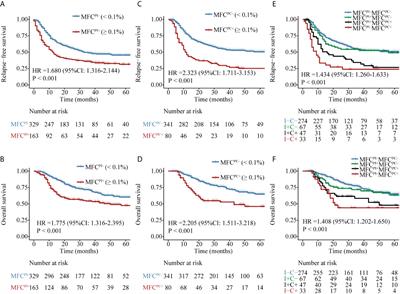
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Apr 2022

REVIEW
Published on 17 Feb 2022
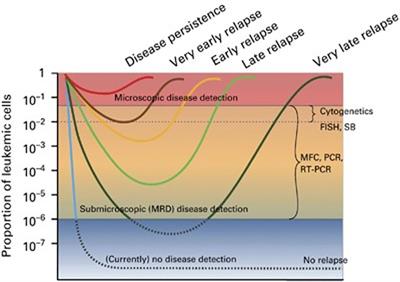
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Jan 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 May 2021