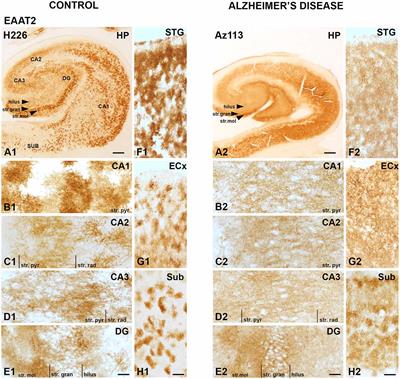
EDITORIAL
Published on 17 Aug 2022
Editorial: The known, the unknown, and the future of glutamate transporters
doi 10.3389/fncel.2022.1005834
- 1,320 views
- 1 citation
10k
Total downloads
46k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 17 Aug 2022
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 03 Jun 2022
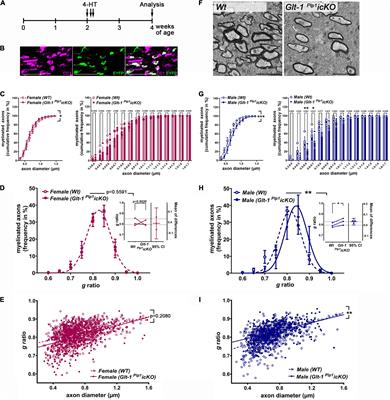
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 09 May 2022
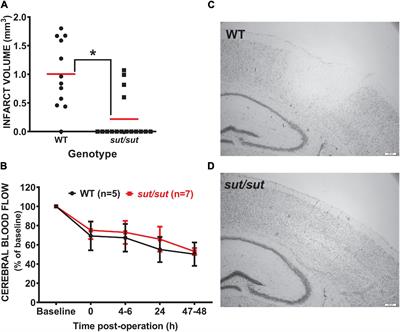
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Mar 2022
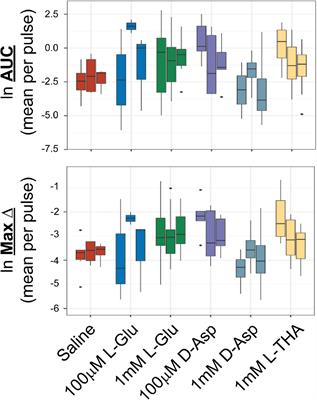
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 Jan 2022
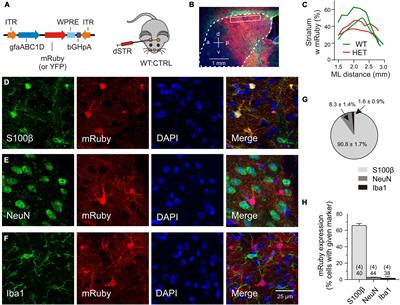
REVIEW
Published on 13 Jan 2022
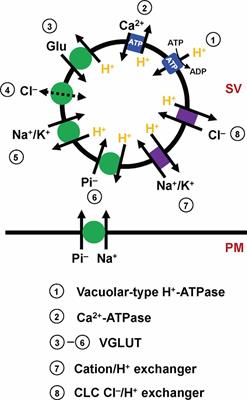
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 Jan 2022
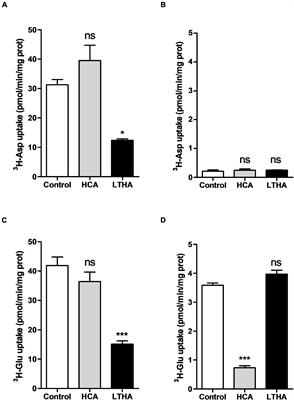
REVIEW
Published on 06 Jan 2022
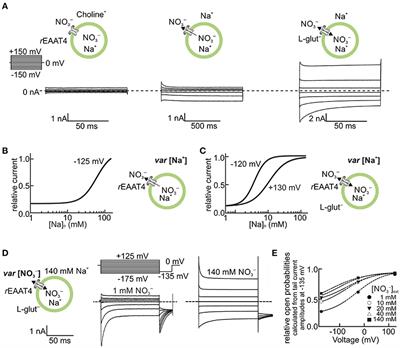
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 29 Dec 2021
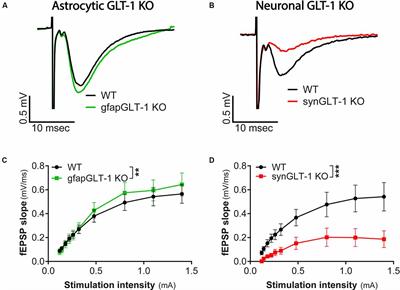
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Dec 2021
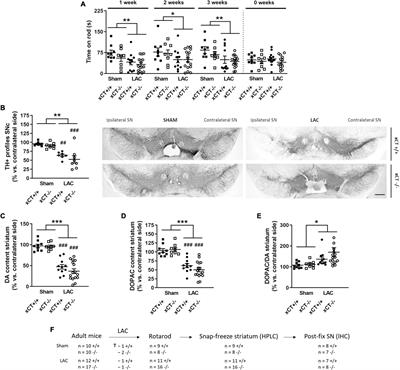
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 Sep 2021