EDITORIAL
Published on 03 Aug 2022
Editorial: Metabolic regulation in cardiovascular homeostasis and disease
doi 10.3389/fcvm.2022.995207
- 1,134 views
- 1 citation
18k
Total downloads
69k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 03 Aug 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 May 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 07 Feb 2022
REVIEW
Published on 23 Dec 2021

REVIEW
Published on 11 Nov 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 29 Sep 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Sep 2021
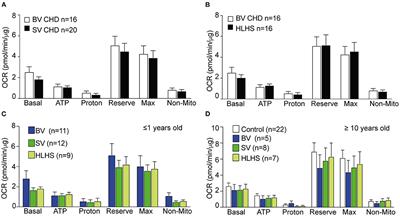
MINI REVIEW
Published on 27 Aug 2021
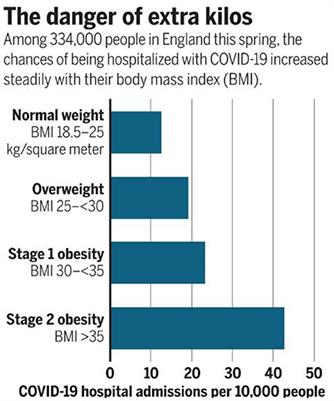
REVIEW
Published on 02 Aug 2021
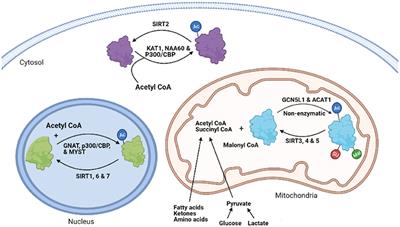
REVIEW
Published on 28 Jul 2021
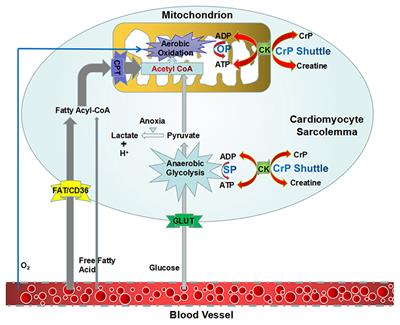
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 May 2021
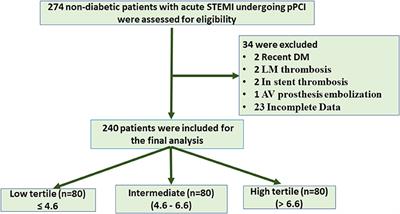
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Apr 2021