EDITORIAL
Published on 03 Sep 2021
Editorial: Novel Applications of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT)
doi 10.3389/fonc.2021.760078
- 973 views
11k
Total downloads
40k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
EDITORIAL
Published on 03 Sep 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 16 Jul 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Jun 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 May 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 27 May 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 29 Apr 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Apr 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Mar 2021
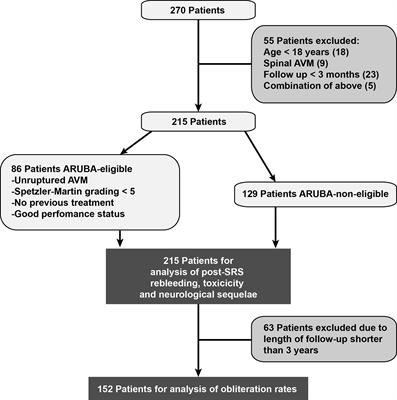
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 25 Feb 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 05 Feb 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Jan 2021

