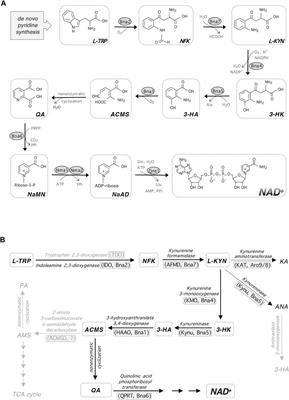
REVIEW
Published on 16 Aug 2021
NAD+ Degrading Enzymes, Evidence for Roles During Infection
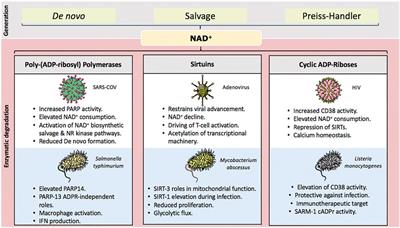
doi 10.3389/fmolb.2021.697359
- 9,646 views
- 17 citations
9,989
Total downloads
47k
Total views and downloads
REVIEW
Published on 16 Aug 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 26 Jul 2021

REVIEW
Published on 08 Jul 2021
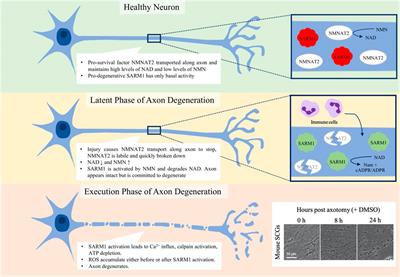
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Jul 2021
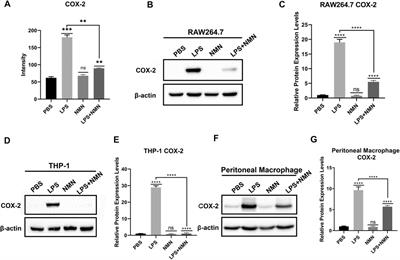
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 19 May 2021