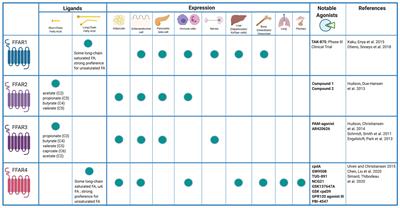
EDITORIAL
Published on 16 Mar 2022
Editorial: Free Fatty Acids as Signaling Molecules: Role of Free Fatty Acid Receptors and CD36

doi 10.3389/fphys.2022.862458
- 2,542 views
- 5 citations
16k
Total downloads
65k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 16 Mar 2022

REVIEW
Published on 01 Jul 2021

MINI REVIEW
Published on 24 May 2021
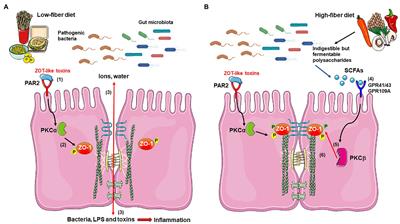
REVIEW
Published on 28 Apr 2021

REVIEW
Published on 08 Apr 2021
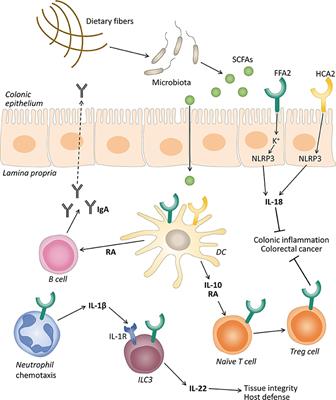
MINI REVIEW
Published on 07 Apr 2021