EDITORIAL
Published on 07 Feb 2022
Editorial: EMG/EEG Signals-Based Control of Assistive and Rehabilitation Robots
doi 10.3389/fnbot.2022.840321
- 3,360 views
14k
Total downloads
69k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 07 Feb 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
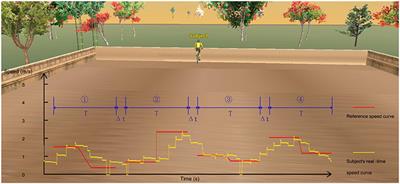
Published on 23 Nov 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 05 Nov 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 03 Nov 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 29 Oct 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 25 Oct 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Sep 2021
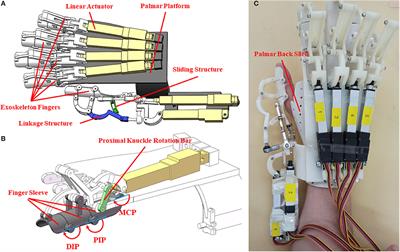
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 02 Aug 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 16 Jul 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 May 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 11 Jan 2021
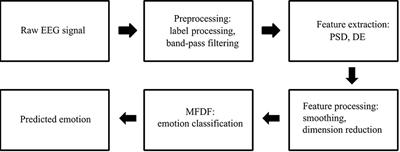
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 Nov 2020