ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 05 Nov 2021
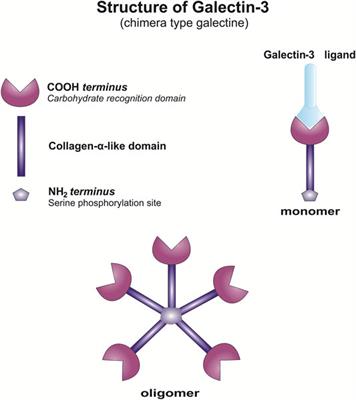
Transgenic Overexpression of Galectin-3 in Pancreatic β Cells Attenuates Hyperglycemia in Mice: Synergistic Antidiabetic Effect With Exogenous IL-33
doi 10.3389/fphar.2021.714683
- 1,707 views
- 6 citations
6,728
Total downloads
20k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 05 Nov 2021

BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 30 Aug 2021
REVIEW
Published on 17 May 2021
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 20 Apr 2021
MINI REVIEW
Published on 19 Mar 2021