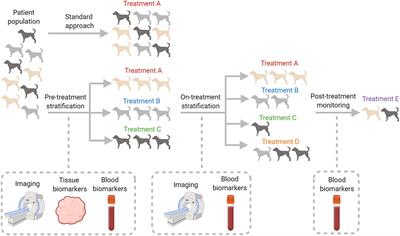
EDITORIAL
Published on 14 Jul 2021
Editorial: Precision Medicine in Veterinary Oncology
doi 10.3389/fvets.2021.718891
- 2,084 views
- 3 citations
16k
Total downloads
83k
Total views and downloads
You will be redirected to our submission process.
EDITORIAL
Published on 14 Jul 2021
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 08 Jul 2021
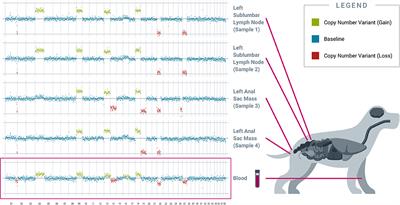
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 12 Apr 2021
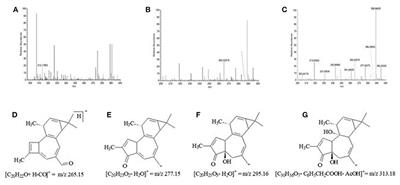
REVIEW
Published on 23 Mar 2021
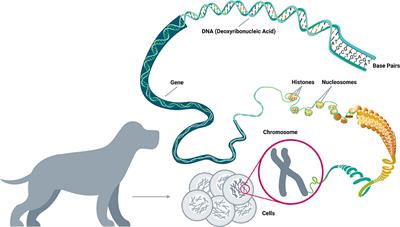
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 25 Feb 2021
REVIEW
Published on 17 Feb 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 Jan 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 05 Jan 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 26 Nov 2020
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Published on 16 Nov 2020
REVIEW
Published on 12 Nov 2020