ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 25 Apr 2022
TMPRSS12 Functions in Meiosis and Spermiogenesis and Is Required for Male Fertility in Mice
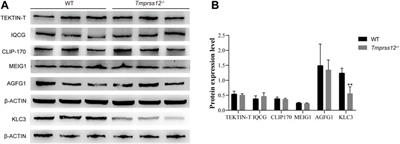
doi 10.3389/fcell.2022.757042
- 2,342 views
- 3 citations
32k
Total downloads
195k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 25 Apr 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Nov 2021
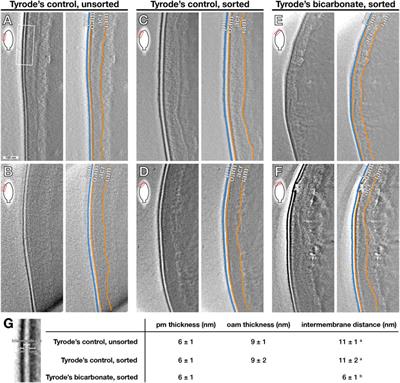
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Nov 2021
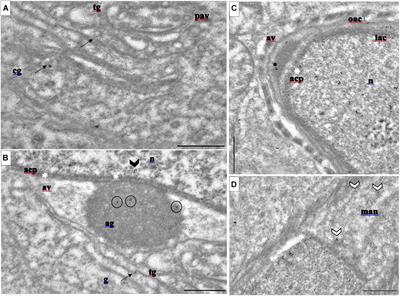
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 18 Oct 2021
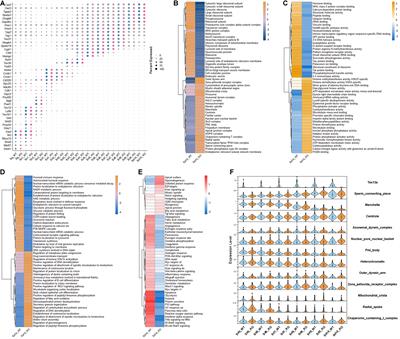
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 29 Sep 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Sep 2021
REVIEW
Published on 20 Jul 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 May 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 23 Apr 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Apr 2021

METHODS
Published on 21 Apr 2021

REVIEW
Published on 16 Feb 2021
