ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 30 Jun 2022
Movement, Behavior, and Habitat Use of Whale Sharks (Rhincodon typus) in the Tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean
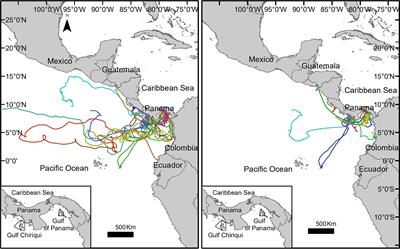
doi 10.3389/fmars.2022.793248
- 13,146 views
- 13 citations
28k
Total downloads
184k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 30 Jun 2022

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Jun 2022
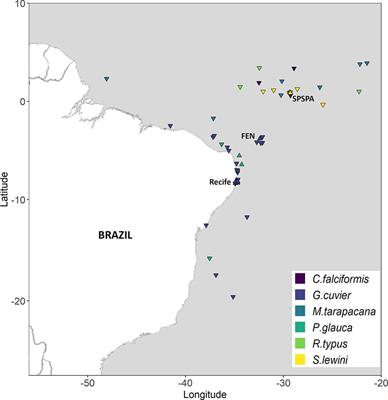
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 25 Feb 2022
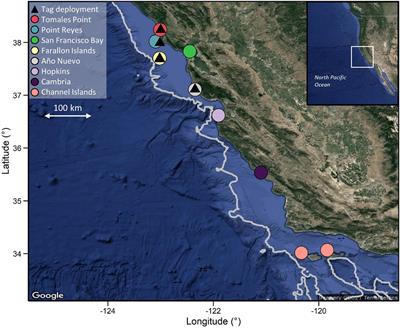
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 18 Nov 2021
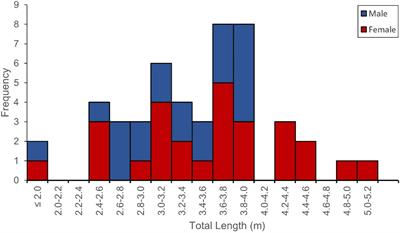
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Sep 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 Aug 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 10 Aug 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Aug 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Jul 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Jul 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Jul 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 26 May 2021
