OPINION
Published on 01 Sep 2021
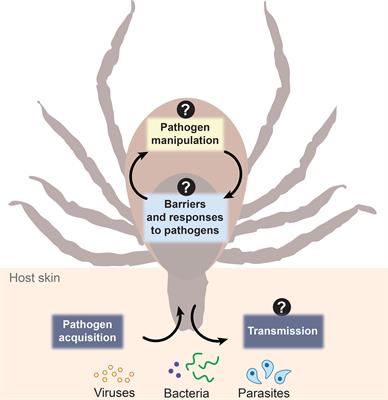
Ticks: More Than Just a Pathogen Delivery Service
doi 10.3389/fcimb.2021.739419
- 3,225 views
- 10 citations
8,397
Total downloads
113k
Total views and downloads
OPINION
Published on 01 Sep 2021

REVIEW
Published on 20 Jul 2021

PERSPECTIVE
Published on 10 May 2021

OPINION
Published on 25 Mar 2021

PERSPECTIVE
Published on 14 Jan 2021

OPINION
Published on 03 Dec 2020
