EDITORIAL
Published on 18 Mar 2022
Editorial: Management of Diabetes and its Complications: A Focus on Endothelial Dysfunction
doi 10.3389/fendo.2022.857983
- 876 views
- 1 citation
13k
Total downloads
40k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 18 Mar 2022
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 09 Nov 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 31 May 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 May 2021
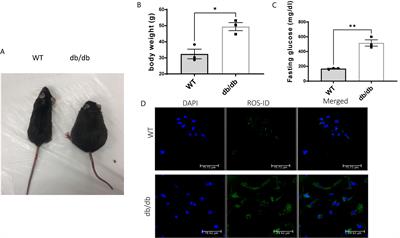
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 14 Apr 2021

REVIEW
Published on 18 Feb 2021

REVIEW
Published on 04 Sep 2020
