EDITORIAL
Published on 24 Mar 2022
Editorial: Immunological Effects of Nano-Imaging Materials

doi 10.3389/fimmu.2022.886415
- 1,178 views
21k
Total downloads
75k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 24 Mar 2022

MINI REVIEW
Published on 06 Jan 2022
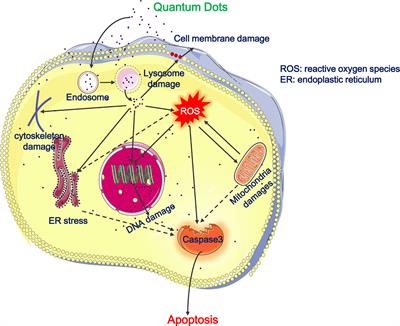
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 07 Oct 2021

MINI REVIEW
Published on 04 Oct 2021

PERSPECTIVE
Published on 14 Sep 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Aug 2021

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 15 Jul 2021

MINI REVIEW
Published on 15 Jun 2021

MINI REVIEW
Published on 03 Jun 2021

MINI REVIEW
Published on 26 May 2021
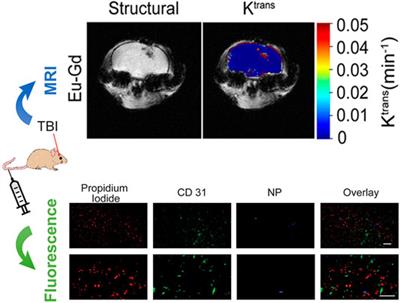
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Apr 2021

MINI REVIEW
Published on 16 Feb 2021

