EDITORIAL
Published on 01 Sep 2021
Editorial: Epigenetic Mechanisms and Their Involvement in Rare Diseases
doi 10.3389/fgene.2021.755076
- 2,475 views
- 11 citations
32k
Total downloads
147k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 01 Sep 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Aug 2021
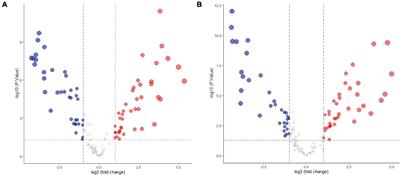
REVIEW
Published on 23 Apr 2021
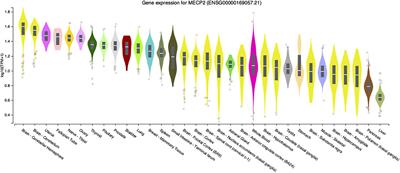
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Apr 2021
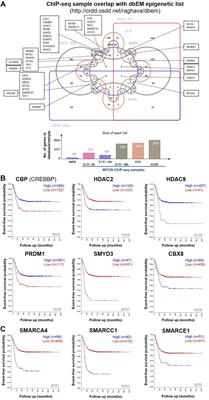
REVIEW
Published on 15 Feb 2021
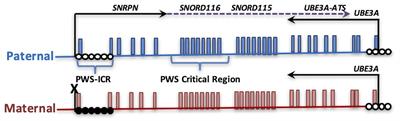
REVIEW
Published on 21 Jan 2021
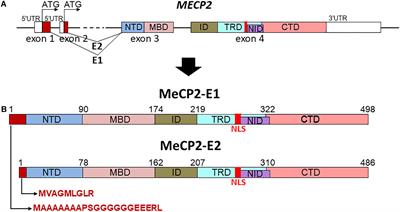
REVIEW
Published on 08 Jan 2021
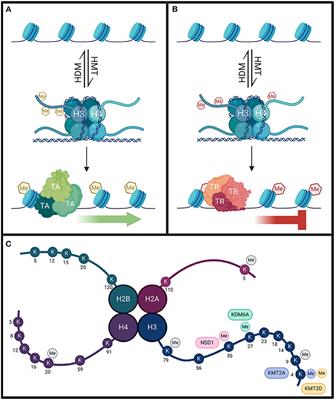
REVIEW
Published on 23 Nov 2020
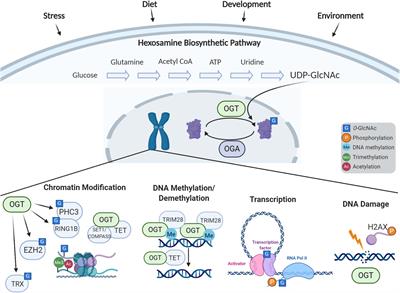
REVIEW
Published on 15 Sep 2020
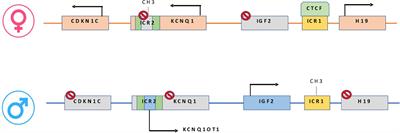
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Aug 2020

REVIEW
Published on 11 Aug 2020
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 01 Jul 2020

