ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Nov 2020
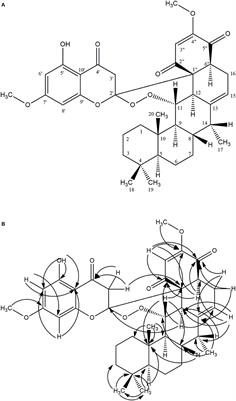
Antiparasitic and Cytotoxic Activity of Bokkosin, A Novel Diterpene-Substituted Chromanyl Benzoquinone From Calliandra portoricensis
doi 10.3389/fchem.2020.574103
- 3,672 views
- 15 citations
6,373
Total downloads
27k
Total views and downloads
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Nov 2020

CORRECTION
Published on 19 Aug 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 04 Aug 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 May 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 16 Apr 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 20 Mar 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 18 Feb 2020

REVIEW
Published on 10 Jan 2020
