EDITORIAL
Published on 18 Jan 2021
Editorial: Antimicrobial Use, Antimicrobial Resistance, and the Microbiome in Food Animals
doi 10.3389/fvets.2020.638781
- 1,434 views
- 2 citations
19k
Total downloads
88k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 18 Jan 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Dec 2020

REVIEW
Published on 03 Sep 2020
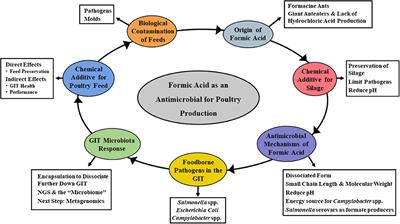
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 19 May 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Apr 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 22 Apr 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Feb 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 28 Feb 2020

BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT
Published on 28 Feb 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 26 Feb 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Feb 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 29 Jan 2020
